Solar System
Describe and explain the creation of the universe, the movements of the Earth and its effects (day, night, seasons, day and polar night)
Solar System
Describe and explain the creation of the universe, the movements of the Earth and its effects (day, night, seasons, day and polar night)
How many years old is the universe? How many years old is planet earth?
TASK 1: THE BIG BANG
Watch the video below and answer the questions.
How many years ago did the big bang occur?
Describe “cosmic background radiation”.
What is “red-shift”?
How did this help to confirm our understanding of the big bang?
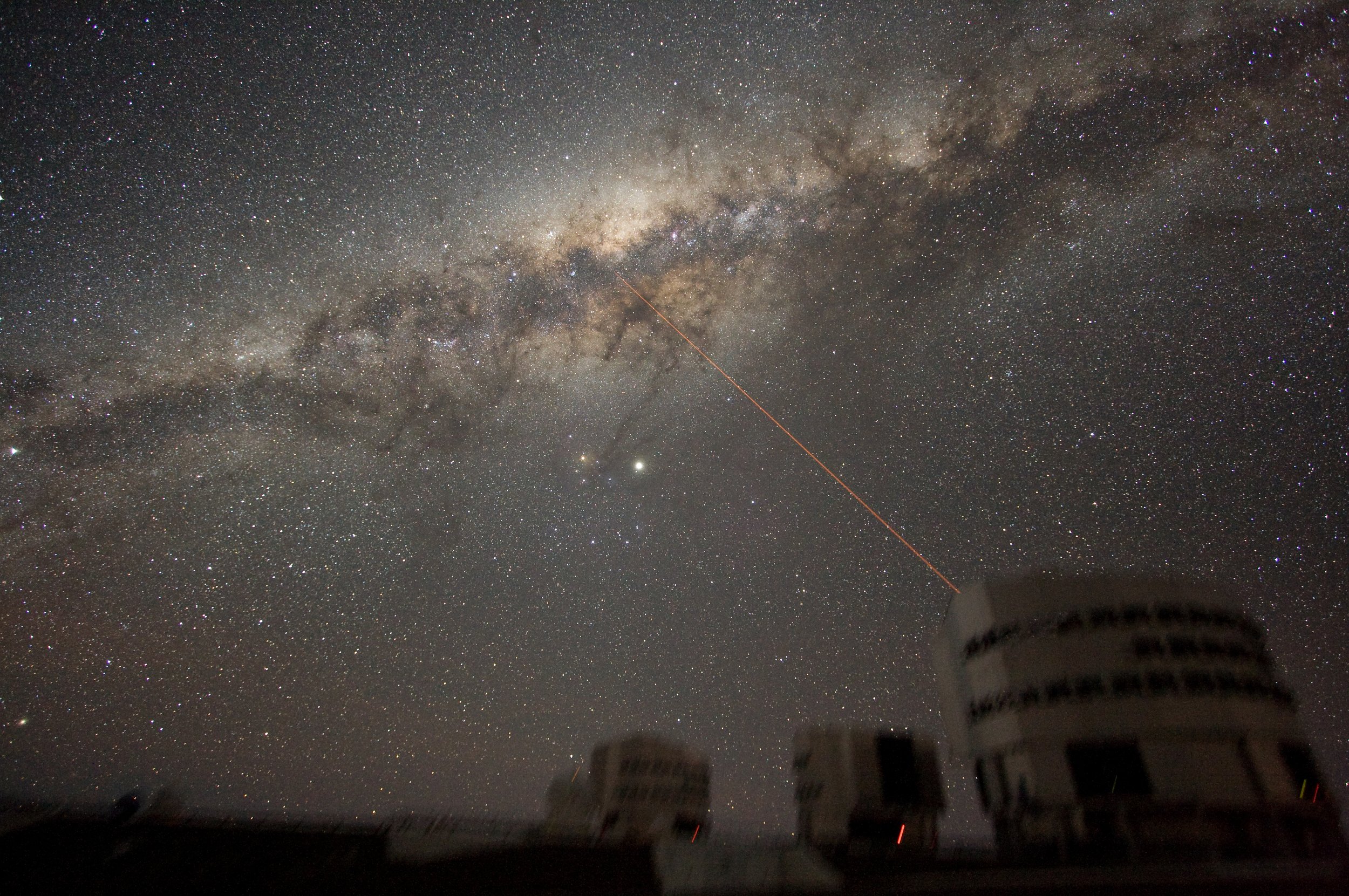
TASK 2: THE MILKY WAY
The Milky Way Galaxy is a large spiral galaxy
It is roughly 100,000 light-years in diameter
It contains Earth’s solar system.
It contains large amounts of dark matter and a massive black hole at its core.
The Sun lies in one of the Galaxy’s spiral arms, about 27,000 light-years from the centre.
TASK 3: PLANETS & THE SOLAR SYSTEM
Watch the video below and complete the worksheet.
TASK 4: GEOCENTRIC vs HELIOCENTRIC
Summarise the theories of Ptolemy and Copernicus
Copernicus’ heliocentric model (left) versus the previous geocentric model proposed by Ptolemy (right)
Claudius Ptolemy was a 2nd century Greek mathematician, astronomer and geographer famous for his controversial geocentric theory of the universe which argued that the earth was at the centre of the universe. This would form the basis of our understanding of the motions of stars and planets for over than a thousand years.
Nicolaus Copernicus was a Renaissance mathematician and astronomer who formulated a model of the universe that placed the Sun rather than Earth at its centre (heliocentric).
TASK 5: ROTATION, REVOLUTION
Define “axis”.
What is “rotation” and “revolution”?
How are they similar and different?
Define “orbit”.
TASK 6: EARTH’S ORBIT
The earth’s orbit is not a perfect circle. It has an elliptical shape, which means the planets can be closer or further away from the sun at different times in its orbit. This is referred to as perihelion and aphelion.
What is the difference between rotation and revolution?
How long does it take for the earth to make one revolution?
What and when is aphelion?
What and when is perihelion?
Define zenith.
TASK 7: SEASONS & EQUINOXES
Study the diagram below and watch the video explaining the seasons
Make notes explaining how the movement of the earth contributes to seasons
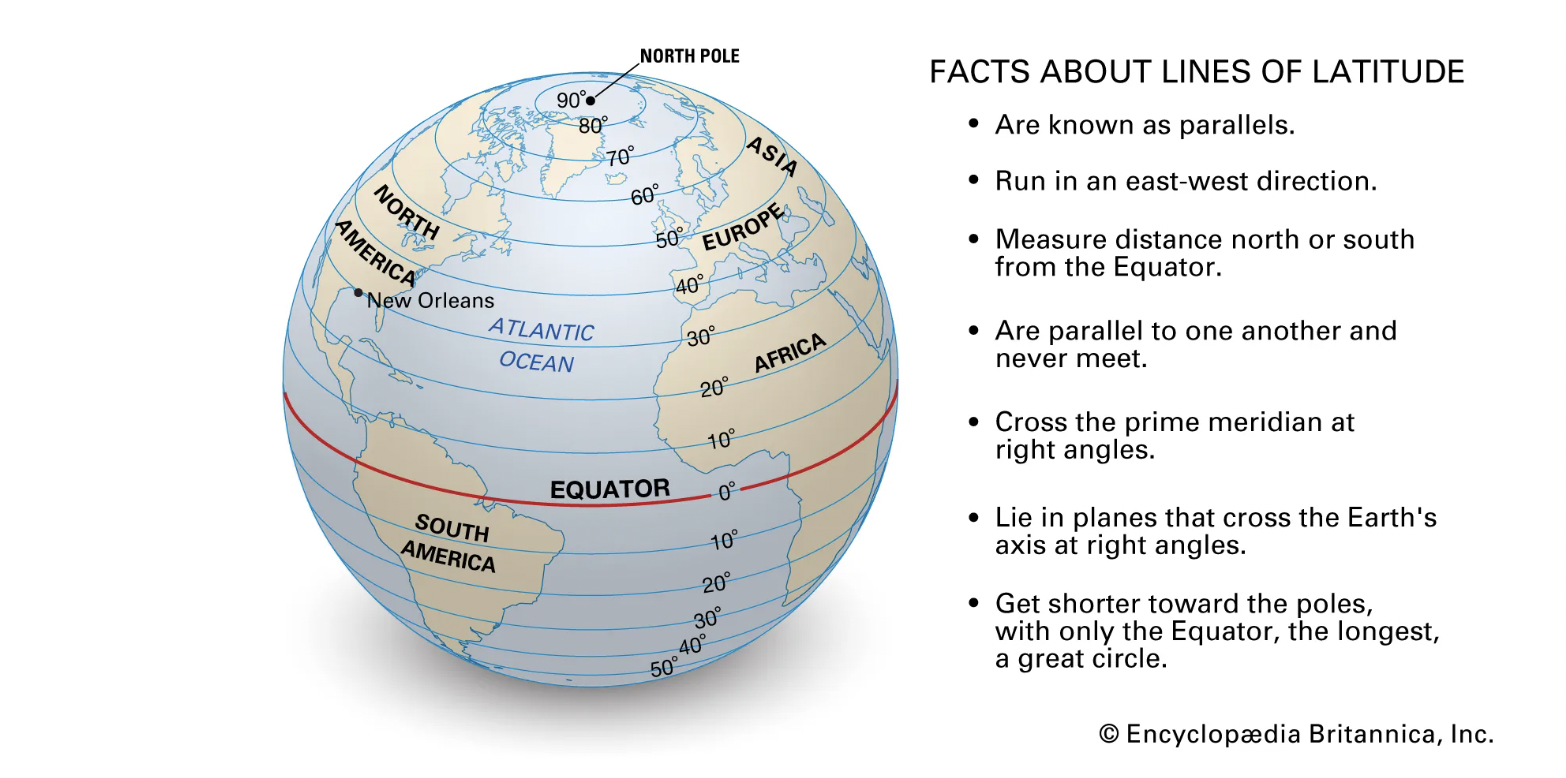
TASK 8: LATITUDE & LONGITUDE
Study the diagrams below
Make a simplified copy of the diagrams and add the information to your notes
TASK 9: REVIEW & PRACTICE
Questions about the solar system in the Maturity exam are always true or false.
Practise your knowledge and understanding of this unit by answering the questions below. If you are not sure about an answer, conduct some online research to help you find the answer.